Section: New Results
Similarity encoding for learning with dirty categorical variables
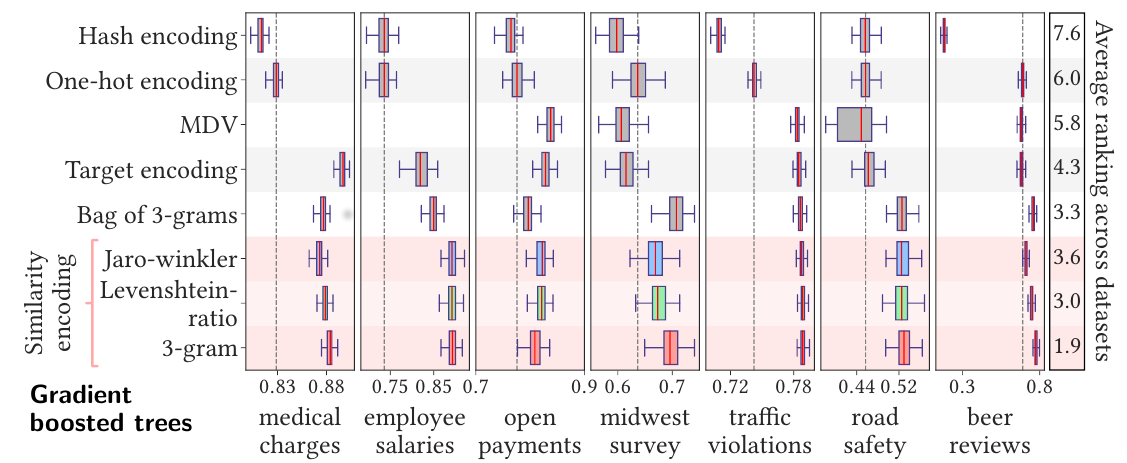
For statistical learning, categorical variables in a table are usually considered as discrete entities and encoded separately to feature vectors, e.g., with one-hot encoding. "Dirty" non-curated data gives rise to categorical variables with a very high cardinality but redundancy: several categories reflect the same entity. In databases, this issue is typically solved with a deduplication step. We show that a simple approach that exposes the redundancy to the learning algorithm brings significant gains. We study a generalization of one-hot encoding, similarity encoding, that builds feature vectors from similarities across categories. We perform a thorough empirical validation on non-curated tables, a problem seldom studied in machine learning. Results on seven real-world datasets show that similarity encoding brings significant gains in prediction in comparison with known encoding methods for categories or strings, notably one-hot encoding and bag of character n-grams. We draw practical recommendations for encoding dirty categories: 3-gram similarity appears to be a good choice to capture morphological resemblance. For very high-cardinality, dimensionality reduction significantly reduces the computational cost with little loss in performance: random projections or choosing a subset of prototype categories still outperforms classic encoding approaches.
|
More information can be found in [7].